CSS
- HTML로는 웹 사이트의 내용을 나열하고 CS로는 웹 문서의 디자인을 구성한다.
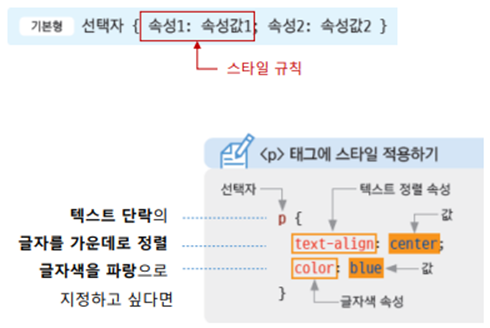
스타일의 형식
CSS의 기본 선택자
| 종류 | 형태 | 사용 예 |
| 전체 선택자 | * | * |
| 태그 선택자 | 태그 | h1 |
| 아이디 선택자 | #아이디 | #id |
| 클래스 선택자 | .클래스 | .header |
| 후손 선택자 | 선택자 선택자 | header h1 |
| 자손 선택자 | 선택자 > 선택자 | header > h1 |
- 문서 안에서 여러 번 반복할 스타일이라면 클래스 선택자로 정의(여러 번 표기 가능)
- 문서 안에서 한번만 사용한다면 id 선택자로 정의
후손 선택자와 자손 선택자
<div>
<h1>h1</h1>
<h2>h2</h2>
<ul>
<li>li1</li>
<li>li2</li>
<li>li3</li>
</ul>
</div>
| 자손 | 후손 |
| div 태그를 기준으로 바로 한 단계 아래에 위치한 h1, h2, ul | div 태그 아래에 위치한 모든 태그 h1, h2, ul, li |
1. 속성 선택자
- input태그를 선택할 때는 속성 선택자를 많이 사용한다. (input은 type 속성에 따라 형태가 다르기 때문)
| 선택자[속성=값] | 특정한 속성 내부 값이 특정 값과 같은 태그 선택 | input[type="text"] |
| 선택자[속성$=값] | 특정 값으로 끝나는 태그를 선택 | input[name$=id] |
| 선택자[속성^=값] | 특정 값으로 시작하는 경우 | input[name^=user] |
| 선택자[속성*=값] | 특정 값이 포함된 경우 | input[type*=t] |
예제1)
1.HTML 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>속성선택자</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>선택자1</li>
<li class="c">선택자2</li>
<li>선택자3</li>
<li class="c">선택자4</li>
<li>선택자5</li>
<li class="c">선택자6</li>
<li>선택자7</li>
</ul>
<img src="../img/img1.jpg">
<img src="../img/img2.jpg" title="nature"/>
</body>
</html>
2) css 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
body {margin:0px;}
.c{ background: #FFEDED; } /*class 선택자 사용*/
img{width:200px; height:200px;}
img[title=nature] { border:3px solid navy; } /*title이 nature인 img 선택*/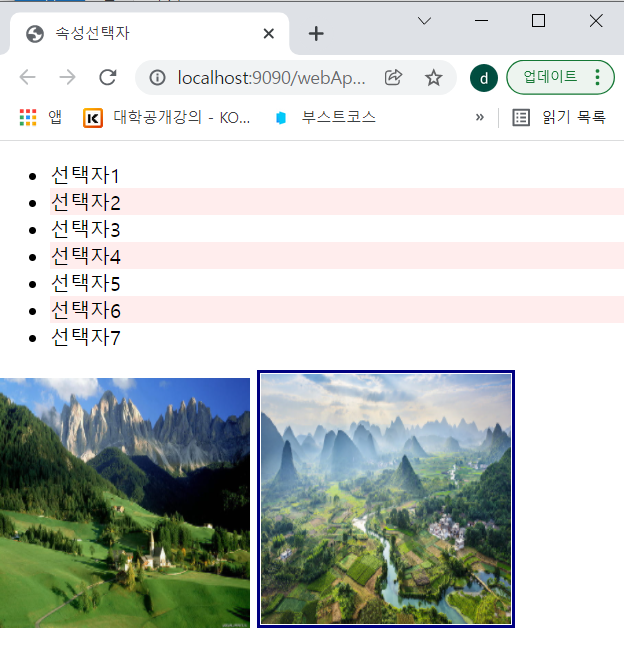
예제2)
1. HTML 파일에 form 추가
<form>
아이디: <input type="text" name="userid"/><br/>
이름: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="login"/>
<hr/>
</form>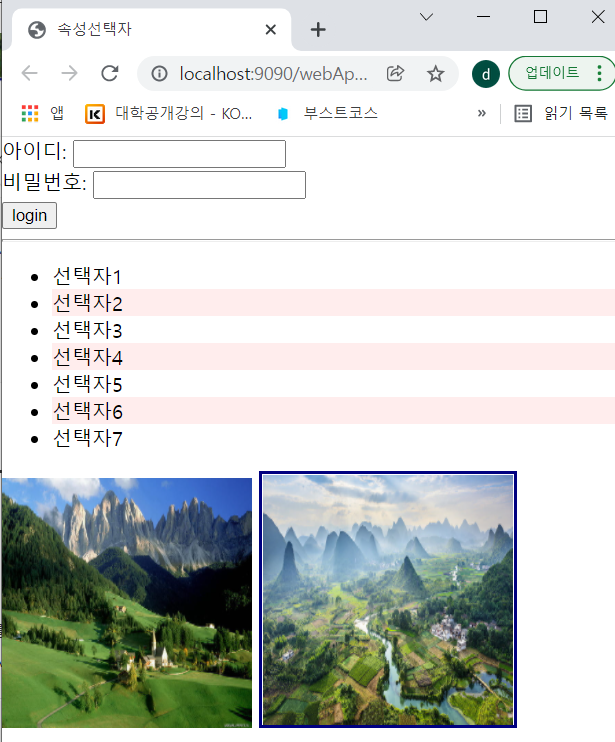
2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
body {margin:0px;}
.c{ background: #FFEDED; } /*class 선택자 사용*/
img{width:200px; height:200px;}
img[title=nature] { border:3px solid navy; } /*title이 nature인 img 선택*/
form>input[name$=id] { /*input태그의 name속성값이 id로 끝나는 값*/
background-color: #F5EEDC !important; /*!important 다른 스타일보다 이 스타일이 우선!*/
}
form>input[name^=user] { /*input태그의 name속성값이 user로 시작하는 값*/
color: orange;
}
form>input[type*=t] { /*input태그의 type의 속성값중에서 t가 포함되어 있는 값*/
background-color: lightblue;
}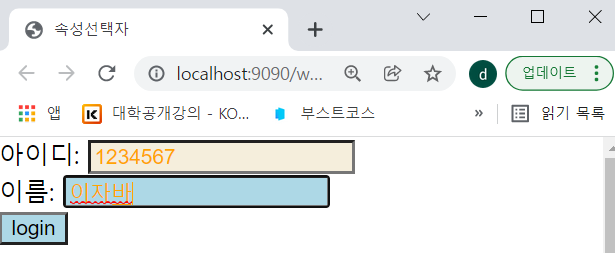
- 만약에 !import가 없으면 아이디의 background도 lightblue가 된다.
2. 반응 선택자
- 반응선택자는 사용자 반응으로 생성되는 특정한 상태를 선택한다.
- 예) 사용자가 특정 태그 위에 마우스 커서를 올리면 hover 상태, 특정 태그를 마우스로 클릭하면 active 상태
| 선택자:active | 사용자가 마우스로 클릭한 태그 선택 | div:active |
| 선택자:hover | 사용자가 마우스로 커서를 올린 태그 선택 | div:hover |
예제1) 위에 있는 HTML에서 반응선택자 추가하기
CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
body {margin:0px;}
.c{ background: #FFEDED; } /*class 선택자 사용*/
img{width:200px; height:200px;}
img[title=nature] { border:3px solid navy; } /*title이 nature인 img 선택*/
/*반응선택자: 마우스오버시*/
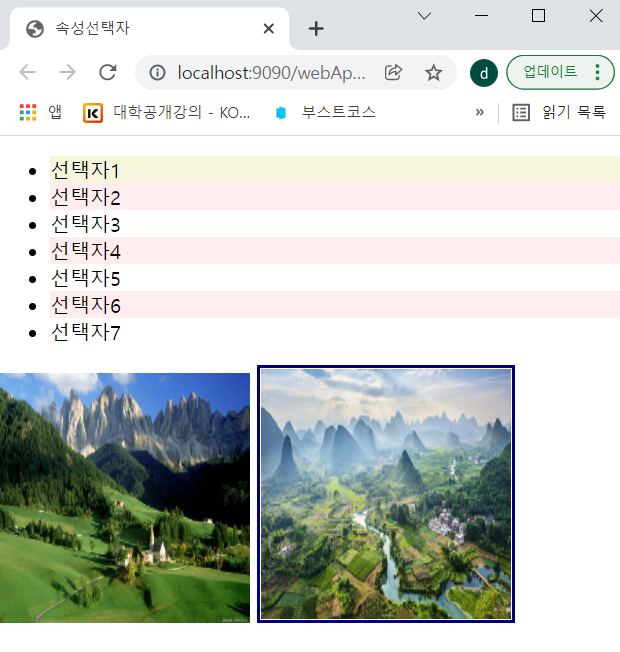
ul>li:hover { /*ul의 자손선택자인 li에 마우스를 올려놓으면 스타일 적용*/
background-color: beige;
}
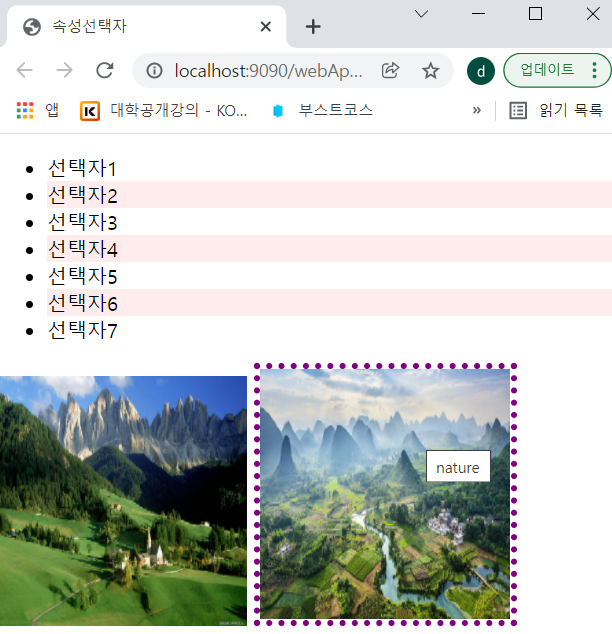
img:hover { /*이미지에 마우스를 올려놓으면 스타일 적용*/
border:5px dotted purple;
}
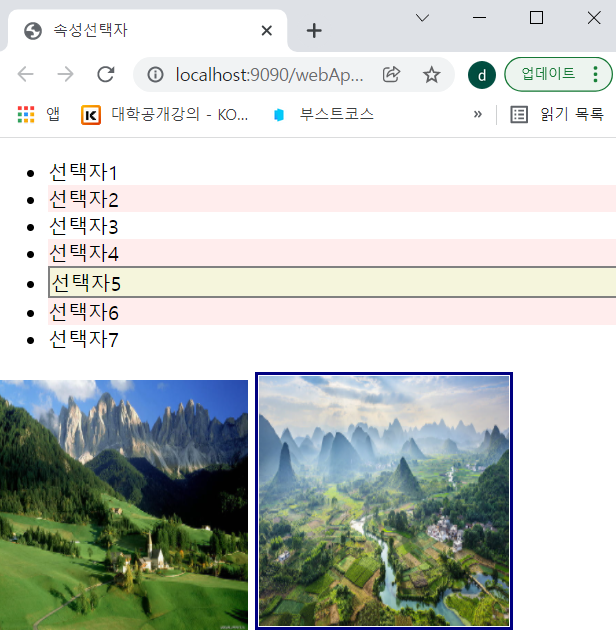
ul>li:active { /*마우스로 클릭하면 스타일 적용*/
border: 2px gray solid;
}1) li에 마우스를 올려놓으면
2) li를 마우스로 클릭하면
3) img에 마우스를 올려놓으면
3. 동위선택자
- 기준이 되는 선택자와 같은 위치에 있는 태그를 선택한다.
- + : 선택자의 다음 객체를 선택 / ~ : 선택자의 다음에 있는 모든 객체
예제)
1. HTML 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>동위선택자</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
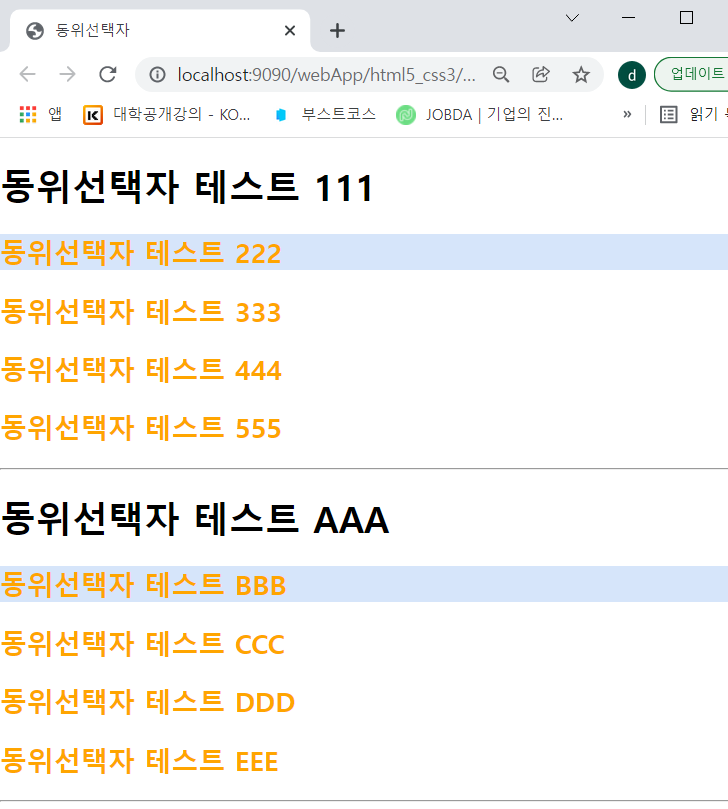
<h1>동위선택자 테스트 111</h1>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 222</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 333</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 444</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 555</h2>
<hr/>
<h1>동위선택자 테스트 AAA</h1>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 BBB</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 CCC</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 DDD</h2>
<h2>동위선택자 테스트 EEE</h2>
<hr/>
</body>
</html>2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
body {margin:0px;}
h1+h2{ /*h1 바로 다음에 있는 h2만 선택*/
background: #D6E5FA;
}
h1~h2 { /*h1 밑에 있는 모든 h2선택*/
color: orange;
}
4. 상태선택자
- 입력 양식의 상태를 선택할 떄 사용한다.
| :checked | 체크 상태의 input 태그 선택 | input:checked |
| :focus | 포커스를 맞춘 input 태그 선택(마우스로 클릭했을 때) | input:focus |
| :enabled / :disabled | 사용 가능한 input 태그 선택 / 사용불가능한 input 태그 | input:enabled / input:disabled |
예제)
1. HTML 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>상태선택자</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<form> <!-- name은 서버언어가 필요한 이름(jsp), id는 프론트언어가 필요한 이름(js) -->
이름: <input type="text" name="username" id="username" value="hong" readonly/><br/>
아이디: <input type="text" name="userid" id="userid" value="hong24" disabled/><br/>
비밀번호: <input type="password" name="userpwd" id="userpwd"/><br/>
관심: <input type="checkbox" name="interest"> 미술
<input type="checkbox" name="interest"> 운동
<input type="checkbox" name="interest"> 음악
<input type="checkbox" name="interest"> 영화
<br/>
취미: <input type="radio" name="hobby"> 그리기
<input type="radio" name="hobby"> 수영
<input type="radio" name="hobby"> 음악 감상
<input type="radio" name="hobby"> 영화 감상
</form>
</body>
</html>
2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
/*disabled와 checkbox, radio는 적용되지 않았다.*/
input:focus {background: beige; font-size:1.2em;}
#username:focus {color: pink;}
/* disabled: 비활성화된 컴포넘트에 적용한다. */
input:disabled { border:2px solid yellow;}
/* checked : 컴포넌트가 checked일 때 적용) */
input:checked {width:40px; height:20px;}
- #username(이름)을 눌렀더니 글자색이 pink가 되었고, input:focus에 의해 background가 beige와 font-size가 커졌다.
- 아이디는 disabled이기 때문에 inut:disabled가 적용되었다.
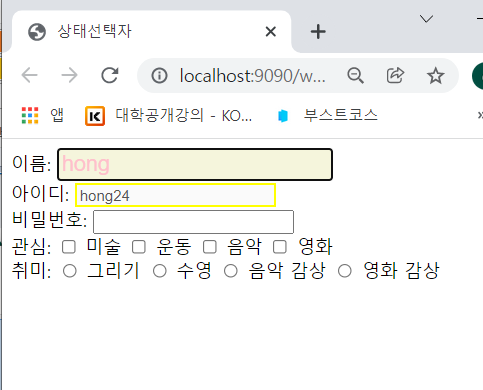
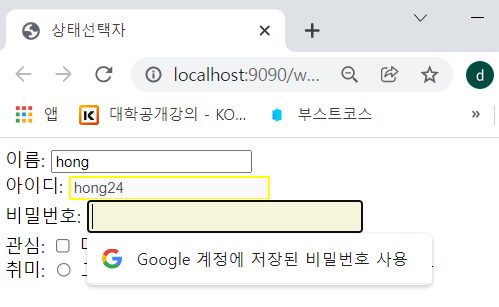
- input:focus에 의해서 비밀번호에도 스타일이 적용되었다.
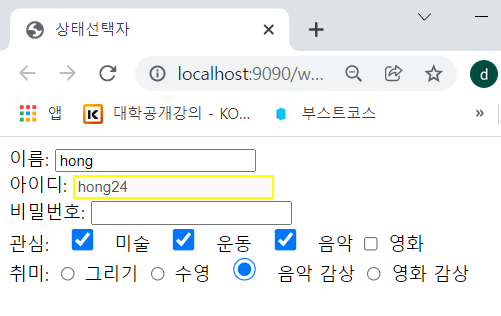
- input:checked에서 check를 했더니 스타일이 적용되었다.
5. 구조선택자
- 특정한 위치에 있는 태그를 선택할 때 사용한다.
| 선택자:first-child | 형제관계에서 첫 번째로 등장하는 태그 선택 |
| 선택자:last-child | 형제관계에서 마지막으로 등장하는 태그 선택 |
| 선택자:nth-child(수열) | 형제관계에서 앞에서 수열번째로 등장하는 태그 선택 |
| 선택자:nth-last-child(수열) | 형제관계에 뒤에서 수열번째로 등장하는 태그 선택 |
- nth-child(수열)에서 수열에는 2n: 짝수번째 객체, 2n+1: 홀수번째 객체, 3n:3의 배수의 객체... 를 선택할 수 있다.
| first-of-type | 처음 객체 |
| last-of-type | 마지막 객체 |
| nth-of-type(2n) | 2n 짝수번째, 2n+1 홀수번째, 3n 3의 배수번째... |
예제)
1. HTML 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>구조선택자</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="list1">
<li>장미</li>
<li>코스모스</li>
<li>민들레</li>
<li>데이지</li>
<li>해바라기</li>
<li>국화꽃</li>
</ul>
<ul id="list2">
<li>장미</li>
<li>코스모스</li>
<li>민들레</li>
<li>데이지</li>
<li>해바라기</li>
<li>국화꽃</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
/*초기화: body랑 ul li는 기본적으로 margin이 있기 때문에 초기화 해준다*/
body ul, li { margin:0px; padding:0px; list-style-type:none;}
/*list1의 자손선택자인 li에 적용될 스타일*/
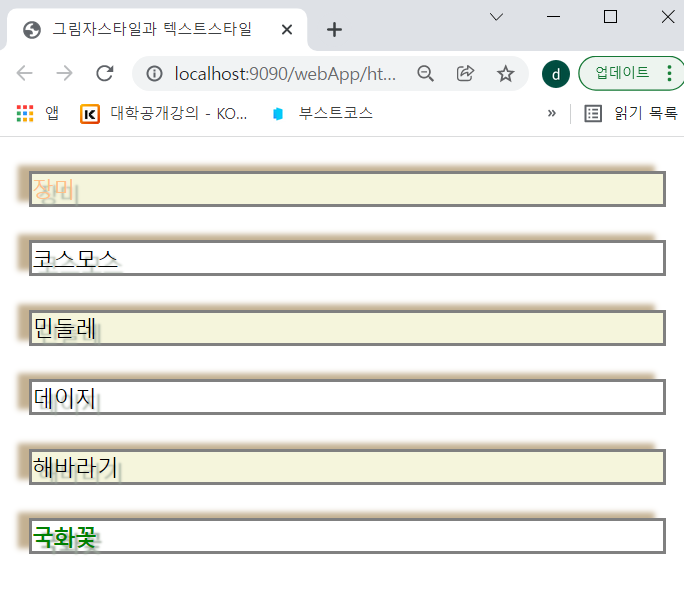
#list1>li:nth-child(2n+1) {background:beige;} /*2의 배수에 background:beige*/
#list1>li:first-child {color:#FFBF86;} /*처음 글자에 color:#FFBF86;*/
#list1>li:last-child {color:green; font-size:1.2em; font-weight:bold;}
/*list2의 자손선택자인 li에 적용될 스타일*/
#list2>li:nth-of-type(2n) {background: #FFDEFA;}
#list2>li:nth-of-type(2n+1) {background: #FFCCD2;}
#list2>li:nth-of-type(4n) {font-weight:bold;} /*4의 배수에 font-weight:bold*/
#list2>li:last-of-type {color:red;} /*마지막 글자에 color:red*/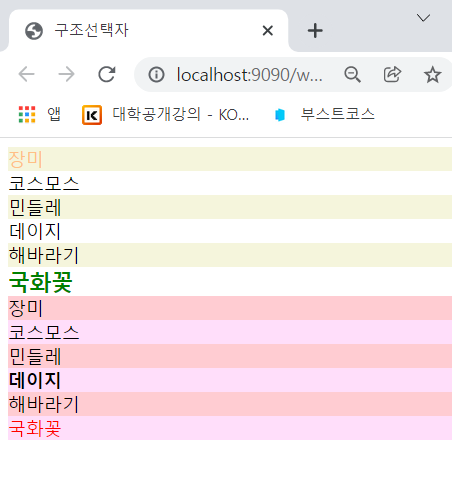
6. 그림자 스타일과 텍스트 스타일
- 그림자 속성: 글자에 그림자를 부여하는 text-shadow 속성, 박스에 그림자를 부여하는 box-shadow 속성
| text-shadow: 5px(오른쪽) 5px(아래) 5px(투명도) black(색상) | box-shadow: 5px(오른쪽) 5px(아래) 5px(투명도) black(색상 |
- 텍스트 스타일
| 선택자::first-letter | 문단의 첫 번째 문자에 스타일 적용 |
| 선택자::first-line | 첫 번째 줄에 적용하는 스타일 |
| 선택자::selection | 선택한 문자의 스타일 |
예제1 ) 그림자 스타일
1. HTML 파일(5번과 동일)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>구조선택자</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="list1">
<li>장미</li>
<li>코스모스</li>
<li>민들레</li>
<li>데이지</li>
<li>해바라기</li>
<li>국화꽃</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
body ul, li { margin:0px; padding:0px; list-style-type:none;}
#list1>li:nth-child(2n+1) {background:beige;}
#list1>li:first-child {color:#FFBF86;}
#list1>li:last-child {color:green; font-size:1.2em; font-weight:bold;}
/*그림자설정 1) 박스 만들기*/
#list1>li { /*위아래:30 왼쪽오른쪽:20*/
font-size:1.2em; margin:30px 20px; border:3px solid gray;
}
/*그림자설정 2) 박스 또는 글자에 그림자표시*/
#list1>li { /*오른쪽 아래쪽 투명 색상*/
/*box-shadow: 10px 5px 5px #C3B091;*/
/*왼쪽 위쪽 투명 색상 -> 반대로 하려면 음수로!! */
box-shadow: -10px -5px 5px #C3B091;
}
#list1>li {
text-shadow: 5px 5px 2px #99A799;
}
예제2 ) 텍스트 스타일
1. HTML 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>그림자스타일과 텍스트스타일</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="newFile.css" type="text/css"></link>
</head>
<body>
<div id="txt">
지난해 가구소득이 600만원을 넘는 고소득자 10명 중 9명은 본인을 '중산층 이하'라고 느끼는 것으로 조사됐다.<br/>
이는 몇 년 새 집값이 천정부지로 오르면서 부동산 유무에 따라 자산 격차가 크게 벌어졌기 때문으로 보인다.<br/>
특히 일부 무주택자는 폭등한 집값으로 인해 하루아침에 '벼락거지' 신세가 됐다고 한탄하고 있다. <br/>
</div>
</body>
</html>2. CSS 파일
@charset "UTF-8";
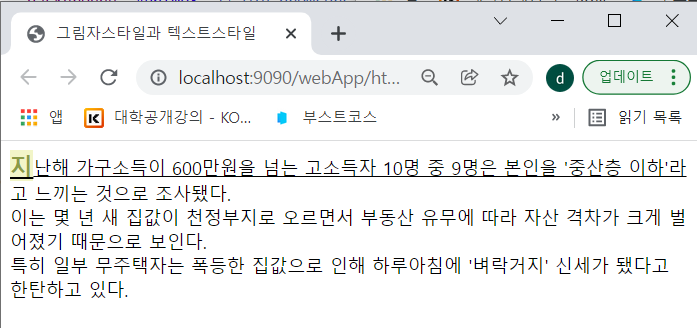
#txt::first-letter {font-size:1.3em; background:#F2F5C8; font-weight:bold; color:#8B9A46;}
#txt::first-line {text-decoration: underline;}
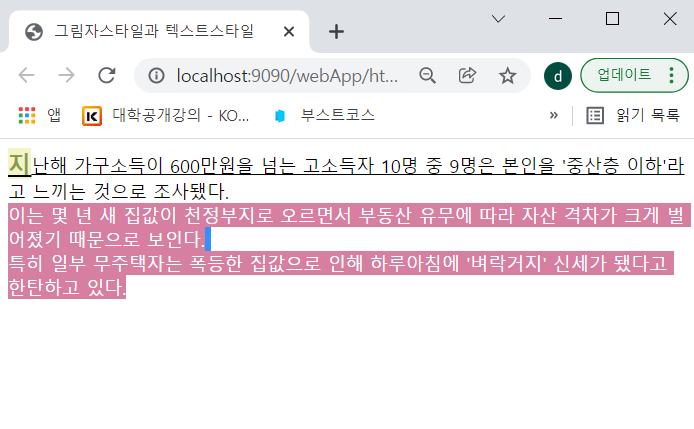
#txt::selection {color:white; background:#D77FA1;} /*드래그 했을 때*/first-letter와 first-line의 스타일이 적용됐다.
selection 스타일이 적용됐다.
- 드래그 못하게 하는 html 태그
- oncontextmenu : 마우스 오른쪽키 사용제어 , onselectstart : 선택시작 불가능(드래그 불가능)
<html oncontextmenu="return false" onselectstart="return false">
스타일 규칙 작성 방법
- 중괄호 ( { } ) 사이에 스타일 규칙 나열
- 규칙이 여러 개일 경우 세미콜론(;)으로 구분
- 주석은 /* 와 */ 사이에 내용을 입력한다.
| CSS 여러 줄로 표기하기 p { text-align: center; color:blue; } |
CSS 한 줄로 표기하기 p { text-align: center; color: blue } |
스타일 시트
| 인라인 스타일 | 스타일 시트(CSS)를 사용하지 않고 스타일을 적용할 대상에 직접 표시 |
| 스타일을 적용하고 싶은 태그에 style 속성을 사용해 style=”속성:속성 값”; 형태로 스타일 적용 | |
| 내부 스타일 시트 | 웹 문서 안에서 사용할 스타일을 문서 안에 정리한 것(html문서의 <head>태그안에) |
| 모든 스타일 정보는 <head>태그안에서 정의하고 <style>태그와 </style>태그 사이에 작성 | |
| 외부 스타일 시트 | 여러 웹 문서에서 사용할 스타일을 별도 파일로 저장해 놓고 필요할 때마다 파일에서 가져와 사용 |
| <style>태그에서 <link>태그만 사용해 미리 만들어 놓은 외부 스타일 시트 파일 연결 |
- 밑에 예제에서 하는 것은 다 내부 스타일 시트이다.
예제)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>tag10_div.html</title>
<style>
body { /*body태그에 있는 모든 것의 margin을 0으로*/
margin: 0px;
}
div { /*모든 div 태그의 width와 height를 200으로, 글자는 orange 굵게, 왼쪽으로*/
width: 200px; /*px, %*/
height: 200px;
color: orange;
font-weight: bold;
float: left; /*정렬 : left, center, right*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color:beige">1</div>
<div style="background-color:rgb(200,250,230)">2</div>
<div style="background-color:#ddd6">3</div>
<div style="background-color:#6dd">4</div>
</body>
</html>margin 속성: 현재 요소 주변의 여백, 마진을 이용하면 요소와 요소 간의 간격 조절 가능하다.
float 속성: 요소를 왼쪽이나 오른쪽에 떠있게 만든다.
float: left
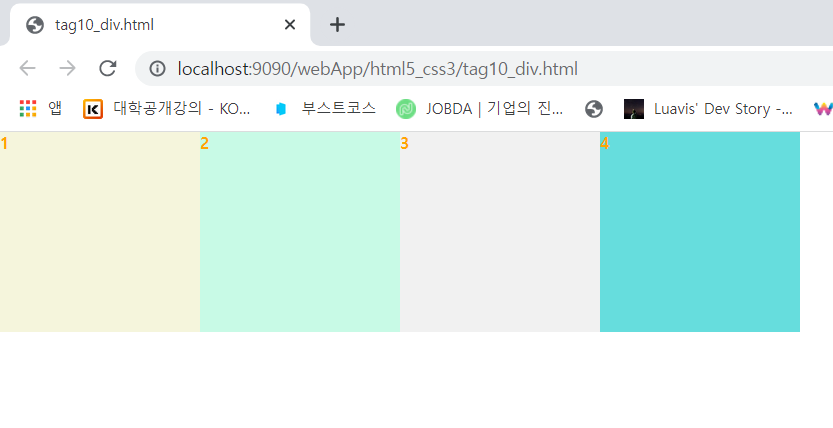
float:center

float: right
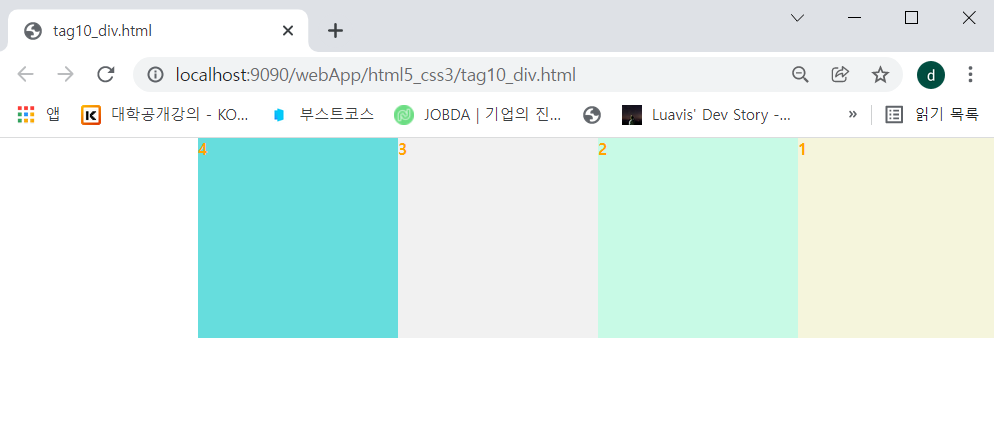
1. left, right, bottom, top속성
- left, right, top, bottom : 각 위치에서 left, right, top, bottom 만큼 떨어지게 만든다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>left,right,top,bottom</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0px;
}
#id1 {
position: absolute; /*포지션이 absolute 포지션이 없으면 실행xx*/
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
left: 100px;
}
#id2 {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
right: 100px;
}
#id3 {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
top: 100px;
}
#id4 {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
bottom: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span id="id1" style="background-color:beige">1</span>
<span id="id2" style="background-color:rgb(200,250,230)">2</span>
<span id="id3" style="background-color:#ddd6">3</span>
<span id="id4" style="background-color:#6dd">4</span>
</body>
</html>
-> 각각 왼쪽 오른쪽 위쪽 아래쪽에서 100px; 떨어져 있다.
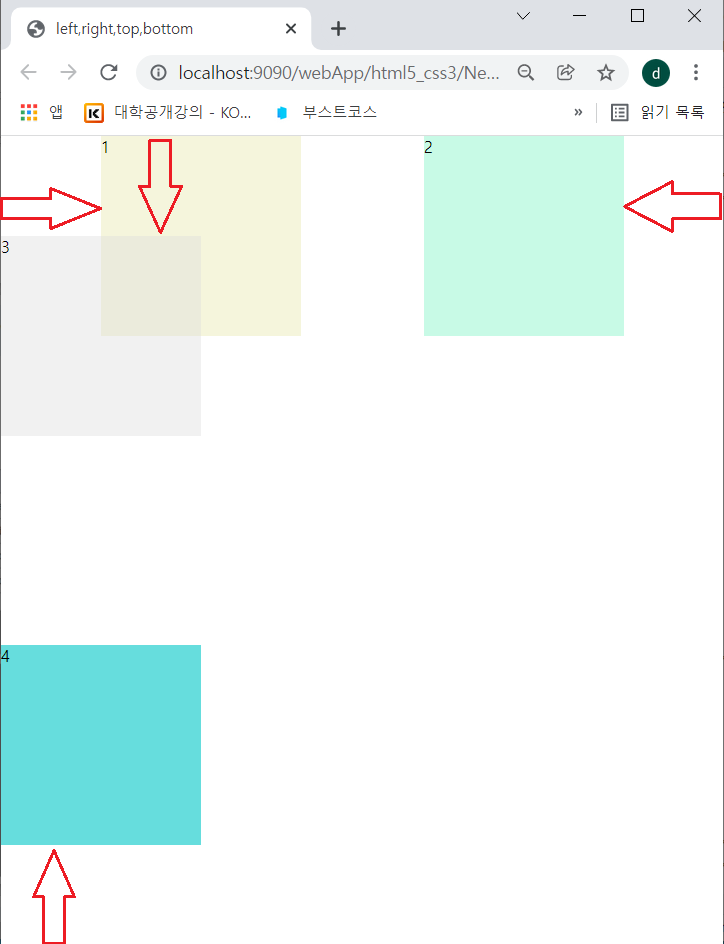
2. Position 속성
- static(기본), absolute(절대좌표), relative(상대 좌표), fixed(고정)으로 나뉘어있다.
| position: static | 요소를 문서의 흐름에 맞춰 배치한다.(기본, 굳이 사용할 필요 없음) |
| position: absolute | 원하는 위치를 지정해 배치한다. |
| position: relative | 이전 요소에 자연스럽게 연결해 배치하되 위치를 지정할 수 있다. |
| position: fixed | 지정한 위치에 고정해 배치한다. 화면에서 요소가 잘릴 수도 있다. |
예제)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>tag11_div2.html</title>
<style>
div { width:200px; height:200px;}
#d1 {
background-color:#FBF8F1;
position:static; /*left, right, top, bottom좌표를 적용하지 않는다.*/
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d2 {
background-color:#F7ECDE;
position:absolute; /*좌표가 적용되고 공간을 반납한다. 둥둥떠있음 */
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d3 {
background-color:rgb(233,218,193);
position:relative; /*현재위치를 기준으로 좌표를 적용하고, 공간을 차지하고 있다.*/
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d4 {
background-color:skyblue;
position:fixed; /*항상 고정, 스크롤이동 시에도 고정 위치를 유지한다. 공간을 반납한다.*/
right:100px; bottom:100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1">AAA</div>
<div id="d2">BBB</div>
<div id="d3">CCC</div>
<div id="d4" style="width:50%; height:200px">DDD</div>
<!-- #d4는 right100px, bottom:100px, width:50%, height:200px모두 적용되었다. -->
</body>
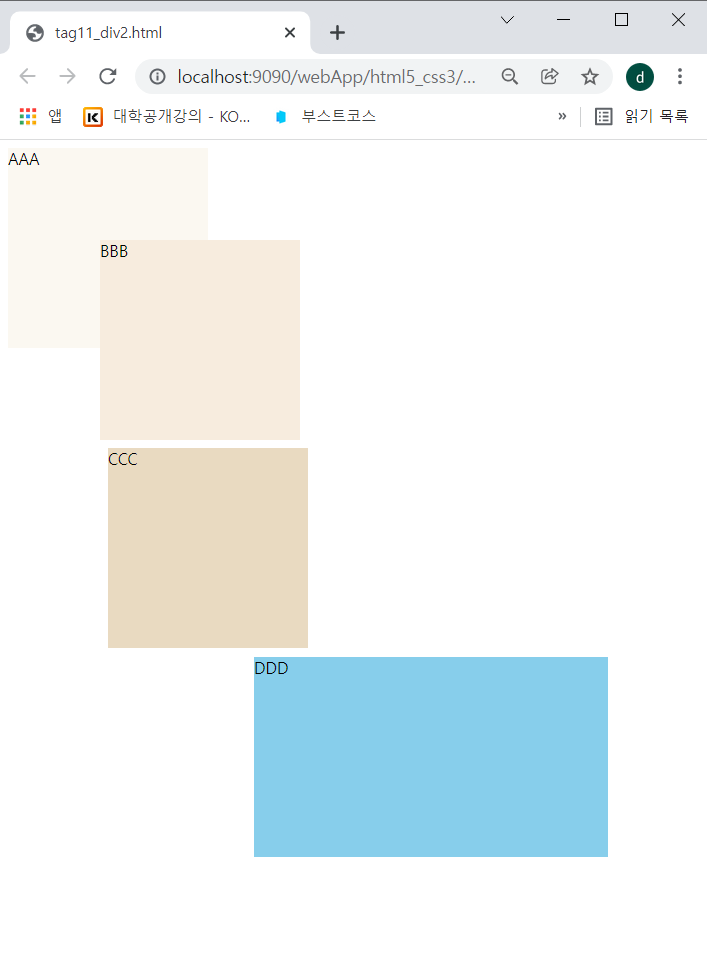
</html>-> #d4는 창을 늘리면 같이 늘려진다.
-> div태그에 의한 스타일은 #d4는 적용되지 않았다. 왜냐하면 직접적으로 style="width:50%; height:200px"; 주었기 때문이다.
예제 2)
<body>
<div id="d1">AAA</div>
<div id="d2">BBB
<div id="d5">bbb</div> <!-- d2의 자손인 d5생성 -->
</div>
<div id="d3">CCC</div>
<div id="d4" style="width:50%; height:80px;">DDD</div>
<div id="d6">EEE <!-- d5 자손 생성 -->
<div id="d7" style="width:100px; height:100px; background-color:#FFF2F9;">eee</div>
</div>
</body>- position이 absolute인 #d2의 자손인 #d5를 생성했다.
- #d6인 div를 새로 생성했다. position을 설정하지 않았기 때문에 position은 static으로 설정되어 있다.
- position이 static인 #d6의 자손인 #d7을 생성했다.
전체 코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>tag11_div2.html</title>
<style>
div { width:200px; height:200px;}
#d1 {
background-color:#FBF8F1;
position:static;
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d2 {
background-color:#F7ECDE;
position:absolute;
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d3 {
background-color:rgb(233,218,193);
position:relative;
left:100px; top:100px;
}
#d4 {
background-color:skyblue;
position:fixed;
right:10px; bottom:10px;
}
#d5{ /*d2의 position이 static이 아니기 때문에 d2가 좌표의 기준이 되었다. */
background-color:rgb(220,230,240);
width:60px; height:60px;
position:absolute;
left:50px; top:50px;
}
#d6{background-color:yellow;} /*position이 static*/
#d7{ /*b6의 position이 static이기 때문에 body가 좌표의 기준이 되었다.*/
position:absolute;
left:50px;top:50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1">AAA</div>
<div id="d2">BBB
<div id="d5">bbb</div> <!-- d2의 자손인 d5생성 -->
</div>
<div id="d3">CCC</div>
<div id="d4" style="width:50%; height:80px;">DDD</div>
<div id="d6">EEE <!-- d5 자손 생성 -->
<div id="d7" style="width:100px; height:100px; background-color:#FFF2F9;">eee</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>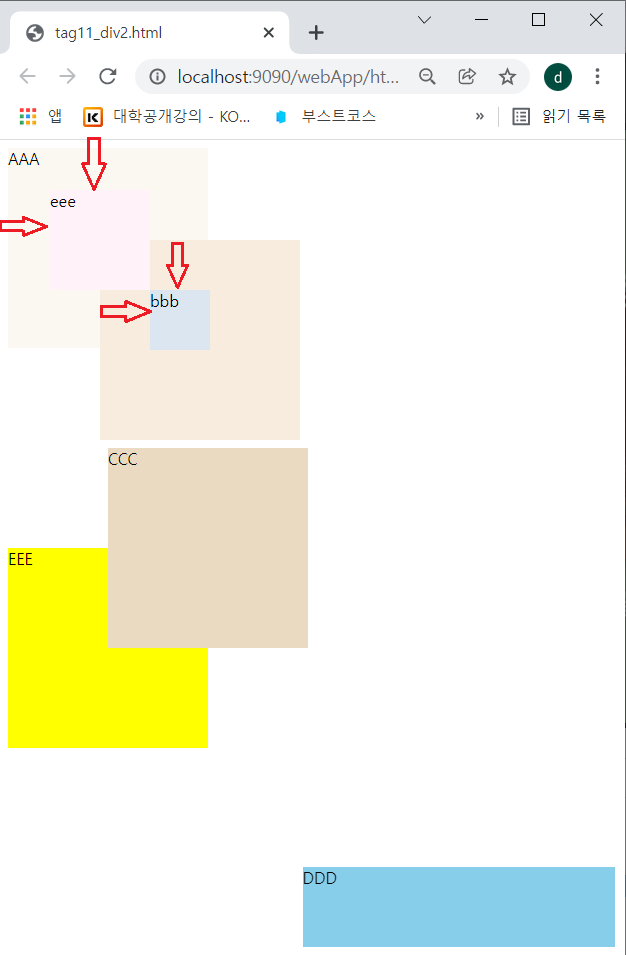
3. Background 속성
| background { } | 모든 background 속성을 이용한 스타일을 한 줄에 설정할 수 있다. |
| background-color | 배경색(값은 color속성의 포맷 사용) |
| background-image | 배경 이미지(이미지 경로를 지정하는 방식으로 사용) |
| background-repeat | 배경 이미지 반복 여부(컨테이너보다 작은 이미지를 적용하면 이미지 반복되어 출력) |
| background-position | 반복되지 않는 배경 이미지의 상대 위치(왼쪽 위부터 이미지를 출력) |
| background-attachment | 위치가 설정된 배경 이미지를 스크롤과는 무관하게 해당 위치에 고정 |
| background-size | 배경 이미지 크기(너비와 높이)를 조정하는 속성 |
background-repeat
- repeat(기본), no-repeat(반복 안 함), repeat-x(수평으로 반복), repeat-y(수직으로 반복)
background-position
| left top: 왼쪽 상단 | left center: 왼쪽 중앙 | left bottom: 왼쪽 맨아래 |
| right top:오른쪽 상단 | right center:오른쪽 중앙 | right bottom: 오른쪽 맨 아래 |
| center top: 가운데 상단 | center (center): 정 가운데 | center bottom: 가운데 맨 아래 |
| x% y% | x는 가로위치, y는 세로 위치 |
| 0% 0% | left top과 같다. |
| 100% 100% | right bottom과 같다. |
| 만약 한가지만 지정하면 나머지는 50%이다. | cm, px, in(inch), pt(point), px, em(16px*n)등의 단위와 섞어서 지정 가능 |
background-attachment
| scroll | 기본값으로, 이미지가 요소에 상대적인 위치 |
| fixed | 이미지가 윈도우 창에 상대적인 위치(스크롤바를 내려도 이미지 위치가 그대로) |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>background</title>
<style>
body {
background-color:#C0D8C0;
background-image:url(../img/img1.jpg);
background-repeat: repeat-y;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-position: 0% 0%;
background-size: 200px 200px;
/*스타일 속성에 대한 그룹화(순서는 상관없다.)
size빼고 위의 코드와 동일 size와 position은 동시에 사용 불가*/
/*background: repeat-y #C0D8C0 url(../img/img1.jpg) 0% 0%;*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>background속성</h1>
<img src="../img/img4.jpg" width="300"/>
</body>
</html>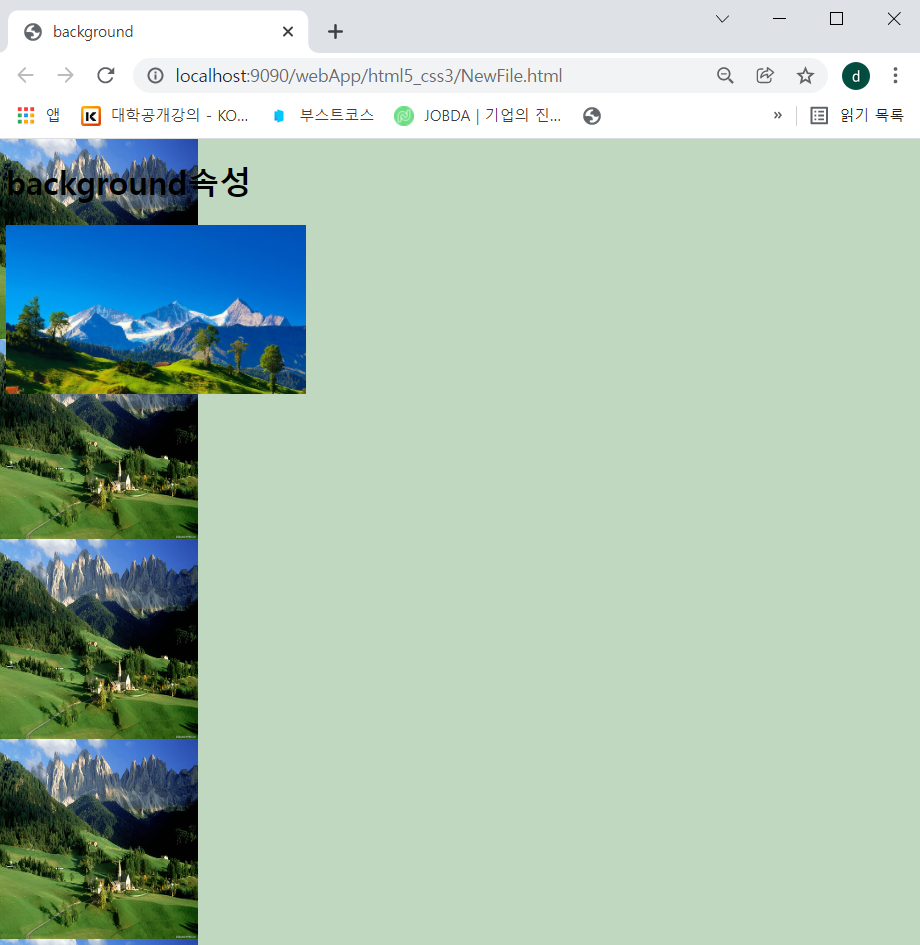
'멀티캠퍼스 풀스택 과정 > 프론트엔드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프론트엔드1-7. CSS 외부 스타일 시트 적용하기(Link와 @import) (0) | 2022.02.05 |
|---|---|
| 프론트엔드1-6. CSS 메뉴 만들기 실습(가상클래스, text-decoration) (0) | 2022.02.05 |
| 프론트엔드1-4. <div> (0) | 2022.02.04 |
| 프론트엔드1-3. 기본태그(form과 input, 그 외 태그들) (0) | 2022.02.04 |
| 프론트엔드1-2. 기본태그(글자,목록,테이블,미디어,MAP) (0) | 2022.02.04 |



